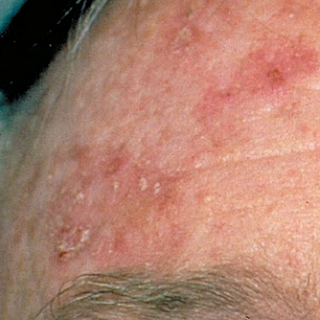
Actinic Keratosis disease
Actinic Keratosis is a condition in which there is a coarse and scaly plaque on the skin, which develops due to chronic exposure to sunlight. This condition is most commonly found on the face, lips, ears, the back of the hand, the forearm, the head, or the neck.
The condition also known as solar keratosis can undergo slow enlargement and generally does not cause signs or symptoms other than a plaque on the skin. The plaque evolved over the years, and first arises generally after the age of 40 years.
Small percentages of lesions arising from iconic keratosis can develop into skin cancers. Decreasing the risk of occurrence of keratosis can be done by minimizing exposure to sunlight and protecting the skin from ultraviolet rays (UV).
Causes of Actinic Keratosis
The Actinic of keratosis can be caused by frequent or intense exposure to UV rays. This condition can happen to anyone, but someone is more prone to experience when there are the following conditions:
- Over 40 years old
- Stay in a location with sunny weather
- Have a history of frequent or intense exposure to sunlight
- Has a vulnerability to experience skin spots or burns when exposed to sunlight
- Have a history of experiencing a keratosis or skin cancer before
- Has a weak immune system as a result of chemotherapy, leukemia, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), or treatment for organ transplantation
Symptoms of Actinic Keratosis
Signs and symptoms of Actinic keratosis can include:
- There are coarse, dry, or scaly plaque on the skin, with a diameter that is generally less than 2.5 centimeters
- Flat plaque with skin or slightly elevated to the outermost layer of the skin
- In some cases, there can be a hard layer of warts and resembles a wart
- Varying lesions colors, including pink, red, or brown
- Itching or burning of the lesions
Actinic keratosis is commonly found in areas exposed to sunlight, such as the face, lips, ears, hands, forearm, head, and neck.
Diagnosis of Actinic Keratosis
Diagnosis of the Actinic of keratosis can generally be determined from a medical interview and PHYSICS examination directly.
If there is any doubt, the doctor can perform a supporting examination, one of which is a skin biopsy. At the time of the biopsy, the doctor can take tissue samples from the skin for further analysis in the laboratory.
ActinicTreatment of Keratosis
The Actinic of keratosis can sometimes subside by itself, but it can also reoccur after exposure to continuing sunlight. Because it is difficult to determine what kind of skin lesions in the Actinic keratosis that can develop into skin cancer, generally carried out the appointment of Acinic Keratosis as a preventative method.
Some of the treatment options that can be done for actinic keratosis are:
- In sufferers with multiple Actinic lesions of keratosis, it is advisable to carry out the treatment of all areas involved. Doctors can prescribe several types of treatment to apply to the skin to relieve complaints.
The side effects of the cream can be reddish, scaly, or burning on the skin for several weeks.
- Photodynamic therapy. In Photodynamic therapy, doctors can apply chemical fluids to certain parts of the skin involved to make them more sensitive to light. Then, the area is then exposed to artificial rays to help destroy the damaged skin cells.
Side effects of this procedure can include redness, swelling, and burning sensations in the skin during therapy.
- Surgery or other procedures. In sufferers with only a few acidic lesions of keratosis, the doctor may recommend an appointment.
One of the methods that can be done is freezing or cryotherapy, in which the actinic keratosis is removed by treating it using nitrogen fluid. The doctor performs the polishing of the substance on the part of the skin involved, which then leads to exfoliation. When the skin begins to heal, the lesion will peel off and the new skin will begin to grow.
Side effects of this procedure can include the onset of wounds, scarring, changes in skin texture, infection, or skin discoloration of the treatment site.
Also, one of the other procedures that can be done is a squirt or a curettage. In this procedure, the doctor uses a tool called a curettage to make the cells damaged.
The airflow can be followed by electrosurgery, where the doctor uses a pencil-like tool to cut and destroy the tissues involved with the electricity. This procedure requires local anesthetic.
Some of the side effects that may arise from this procedure may include infections, scarring, and skin discoloration at the treatment site.
Prevention of Actinic Keratosis
Prevention of the Actinic of keratosis is important to do because the condition can precede the occurrence of cancer or is an early stage of skin cancer. The safety of exposure to sunlight is important to prevent the development and recurrence of plaque or freckles due to Actinic keratosis.
To help protect the skin from exposure to sunlight, some of these things can be done:
- Limit sun exposure time. It is recommended to avoid exposure to sunlight from 10 a.m. to 2 noon, also, it is advisable to avoid prolonged exposure, to prevent burns to the skin or darker skin tone.
Both can cause damage to the skin and increase the risk of occurrence of keratosis and skin cancer. Exposure to sunlight that accumulates over time can also lead to the incidence of keratosis.
- Use sunscreen. The use of sunscreen can help to relieve the development of keratosis. Before traveling to the outdoors, use a wide-spectrum sunscreen.
Experts from the American Academy of Dermatology recommend the use of a broad spectrum resistant sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30. Use sunscreen on any part of the exposed skin, and use lip moisturizers.
Use sunscreen about 15 minutes before sun exposure and repeat use every two hours or more often when swimming or sweating.
- Observe the skin regularly and report changes to the doctor. Check the skin regularly and observe the onset of growth of a lesion or growths on the skin, as well as changes in moles, birthmarks, and so on. Carefully examine the entire body.